Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on stomach hernia. In this article, we will provide you with valuable insights into hiatal hernias, including their definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies. Understanding this condition will empower you to make informed decisions about your health and seek appropriate medical care.
Understanding stomACH Hernia
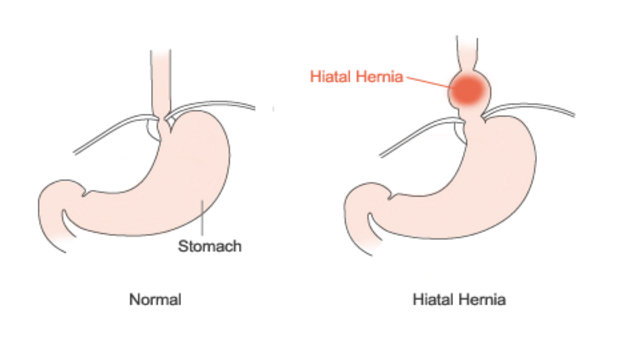
Definition and Causes
A stomach hernia “hiatal hernia” occurs when a portion of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm and into the chest cavity. This condition is usually caused by a weakened or enlarged hiatus, which is the opening in the diaphragm that allows the esophagus to pass through.
Hiatal hernias can be classified into two main types:

- Sliding Hiatal Hernia: This is the most common type of hiatal hernia, where the junction between the esophagus and stomach slides up into the chest.
- Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia: In this type, a portion of the stomach squeezes through the hiatus and lies beside the esophagus.
The exact cause of hiatal hernias is not always clear, but certain factors may contribute to their development. These factors include:
- Weakness in the muscles of the diaphragm due to aging or injury.
- Increased pressure on the abdomen from obesity, pregnancy, or frequent heavy lifting.
- Chronic coughing or straining during bowel movements.
Stomach hernia Symptoms and Diagnosis

Stomach hernias can present with various symptoms, although some individuals may not experience any symptoms at all. Common symptoms of stomach hernias include:
- Heartburn and acid reflux: The protrusion of the stomach into the chest can lead to the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation.
- Chest pain: stomach hernias can cause discomfort and pain in the chest, often resembling heart-related conditions.
- Difficulty swallowing: In some cases, a stomach hernia may compress the esophagus, leading to difficulty or pain while swallowing.
- Belching and regurgitation: Excessive belching and the backflow of stomach contents into the mouth can occur.
To diagnose a stomach hernia, your healthcare provider may conduct a physical examination and order diagnostic tests such as an upper gastrointestinal (GI) series, endoscopy, or pH monitoring.
Treatment Options
Treatment for stomach hernia aims to relieve symptoms and prevent complications. The appropriate treatment approach depends on the severity of symptoms and the size of the hernia. Common treatment options include:
Lifestyle Changes
In mild cases of stomach hernias, lifestyle modifications may be sufficient to manage symptoms. These changes may include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Losing excess weight can help reduce pressure on the abdomen and alleviate symptoms.
- Dietary adjustments: Avoiding trigger foods that worsen acid reflux, such as spicy or fatty foods, caffeine, and alcohol.
- Eating smaller meals: Consuming smaller, more frequent meals can help prevent stomach distension and reduce reflux.
- Posture and sleep modifications: Elevating the head of the bed and maintaining an upright posture after meals can aid in digestion and minimize reflux.
Medications and Therapies
Medications may be prescribed to control acid reflux and manage related symptoms. These may include:
- Antacids: Over-the-counter antacids can provide temporary relief by neutralizing stomach acid.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): PPIs reduce the production of stomach acid, providing long-term relief from symptoms.
- H2 blockers: These medications help reduce acid production and alleviate symptoms.
In addition to medications, your healthcare provider may recommend therapies such as:
- Hietal stomach hernia exercises: Certain exercises can strengthen the diaphragm and improve muscle tone, potentially reducing hernia-related symptoms.
- Speech therapy: For individuals experiencing swallowing difficulties, speech therapy may help improve swallowing coordination.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases or when conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. The two main surgical options for hiatal hernias are:
- Hernia repair: During this procedure, the hernia is pushed back into place, and the hiatus is tightened to prevent future herniation. This may be done using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques.
- Fundoplication: This surgery involves wrapping a portion of the stomach around the lower esophagus to reinforce the lower esophageal sphincter and reduce reflux.

Surgical intervention is usually considered for large hiatal hernias, complications such as strangulation or obstruction, or when symptoms are severe and significantly impact quality of life.
Managing Hiatal Hernia Symptoms
In addition to medical interventions, adopting certain strategies can help manage hiatal hernia symptoms effectively. Here are some recommendations:
Diet and Nutrition
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals to reduce pressure on the stomach.
- Avoid trigger foods that may worsen acid reflux, such as spicy, fatty, and acidic foods.
- Consume meals at least 2-3 hours before lying down to minimize reflux.
- Chew food thoroughly and eat slowly to aid digestion.
- Stay hydrated and drink fluids between meals to prevent overfilling the stomach.
Weight Management
- Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Losing excess weight can alleviate pressure on the abdomen and reduce symptoms.
Posture and Sleep Positions
- Sit upright during and after meals to aid digestion and prevent reflux.
- Use pillows or raise the head of the bed to elevate the upper body while sleeping.
By implementing these lifestyle modifications, individuals with hiatal hernias can experience relief and improved overall well-being.
Prevention and Outlook
While hiatal hernias cannot always be prevented, there are steps you can take to minimize your risk. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Avoiding activities that may increase abdominal pressure, such as heavy lifting.
- Practicing good posture and body mechanics during daily activities.
- Managing conditions that may contribute to the development of hiatal hernias, such as chronic coughing or constipation.
The outlook for individuals with hiatal hernias is generally positive. With appropriate management strategies and medical interventions when necessary, most people can effectively control symptoms and lead a normal life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hiatal hernias are a type of stomach hernia that occur when a portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hiatal hernias is crucial for managing this condition effectively. By making lifestyle modifications, seeking medical care, and implementing symptom management strategies, individuals with hiatal hernias can experience relief and improve their quality of life.
FAQs
- Can a hiatal hernia go away on its own?In most cases, hiatal hernias do not go away on their own. However, lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical interventions can effectively manage symptoms.
- Is a hiatal hernia the same as a stomach hernia?While both involve the protrusion of stomach tissue, a hiatal hernia specifically refers to the protrusion through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
- Can a hiatal hernia cause difficulty breathing?Yes, a large hiatal hernia can compress the lungs and cause shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
- Can exercise worsen a hiatal hernia?Certain exercises, such as heavy lifting or intense abdominal exercises, can increase intra-abdominal pressure and potentially worsen symptoms. It is best to consult with a healthcare provider for exercise recommendations.
- Are hiatal hernias more common in certain age groups?Hiatal hernias are more common in individuals over the age of 50, but they can occur at any age.
Remember, if you suspect you have a hiatal hernia or experience persistent symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.

