Introduction
External hemorrhoids in females can be an uncomfortable and bothersome condition that can affect females. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention measures related to external hemorrhoids in females.
Understanding External Hemorrhoids
Definition and Causes
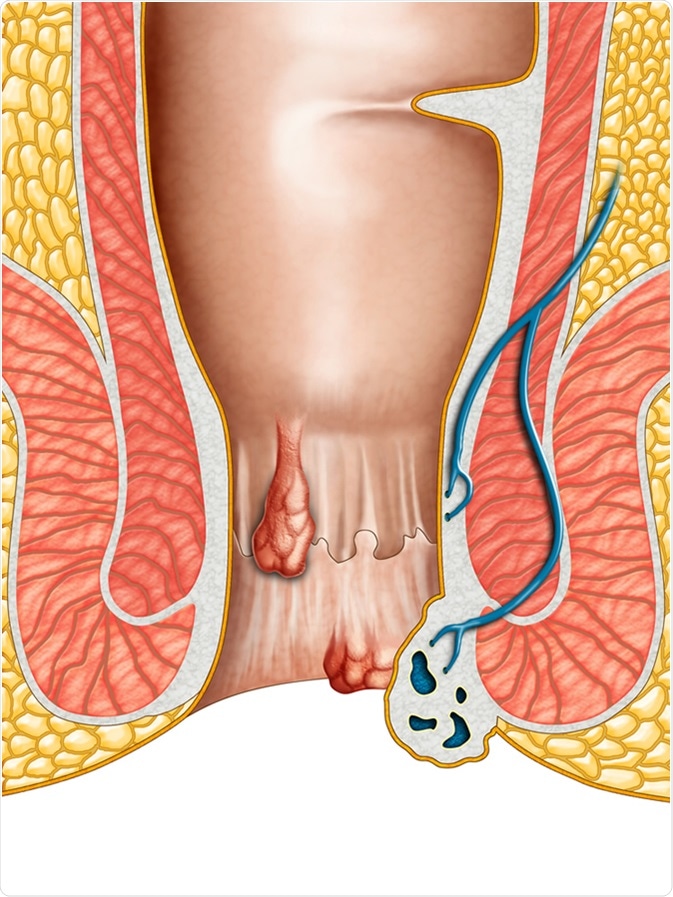
External hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels located around the anus and beneath the skin. They can develop due to increased pressure on the veins in the rectal area. Common causes include straining during bowel movements, prolonged sitting or standing, obesity, and pregnancy.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing external hemorrhoids in females. These include:
- Pregnancy: The pressure on the rectal veins during pregnancy can lead to the development of hemorrhoids.
- Chronic constipation: Straining during bowel movements due to constipation can contribute to the formation of hemorrhoids.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts added pressure on the rectal veins, increasing the likelihood of hemorrhoid development.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Prolonged sitting or standing without adequate movement can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids.
Signs and Symptoms

External hemorrhoids in females can cause various signs and symptoms. These may include:
- Pain or discomfort in the anal area, especially during bowel movements or when sitting for extended periods.
- Itching, swelling, or inflammation around the anus.
- Bleeding during bowel movements.
- A lump or swelling near the anus.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Medical History and Physical Examination
To diagnose external hemorrhoids in females, a healthcare professional will typically start by taking a medical history and conducting a physical examination. They will inquire about symptoms and risk factors and visually inspect the affected area.
Visual Inspection and Proctoscopy
In some cases, a visual inspection of the anus and rectal area may be sufficient for diagnosis. However, if the healthcare professional needs more detailed information, a proctoscopy may be performed. This procedure involves using a specialized instrument called a proctoscope to examine the rectum and lower part of the colon.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for external hemorrhoids in females depend on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s specific circumstances.
Self-Care and Lifestyle Changes
Mild cases of external hemorrhoids can often be managed with self-care measures and lifestyle changes, including:
- Eating a high-fiber diet to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation.
- Drinking an adequate amount of water to stay hydrated.
- Practicing good anal hygiene, such as using moist wipes or gentle cleansing after bowel movements.
- Avoiding excessive straining during bowel movements.
- Engaging in regular physical activity to promote healthy bowel function.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter topical creams, ointments, or suppositories containing ingredients like hydrocortisone or witch hazel may provide temporary relief from itching, swelling, and discomfort associated with external hemorrhoids.
Procedures and Interventions
For more severe or persistent cases, healthcare professionals may recommend procedures or interventions, such as:
- Rubber band ligation: This procedure involves placing a small rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply, causing it to wither and fall off.

- Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is injected into the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink and eventually disappear.

- Hemorrhoidectomy: In rare cases where other treatments have not been effective, surgical removal of the hemorrhoids may be necessary.

Prevention and Outlook
While it may not be possible to prevent external hemorrhoids entirely, several measures can help reduce the risk and minimize symptoms:
- Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Avoiding prolonged sitting or standing and taking breaks to move around.
- Avoiding excessive straining during bowel movements by consuming a high-fiber diet and staying hydrated.
- Practicing good anal hygiene to keep the area clean and prevent irritation.
With proper management and lifestyle modifications, most cases of external hemorrhoids in females can be effectively controlled, and symptoms can be minimized.
Conclusion
External hemorrhoids can cause discomfort and inconvenience for females. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, seeking timely diagnosis and treatment, and implementing preventive measures, women can effectively manage external hemorrhoids and improve their overall well-being.
FAQs
Q1: Are external hemorrhoids a common condition in females? Yes, external hemorrhoids are relatively common in females, especially during pregnancy and in individuals with risk factors such as chronic constipation or obesity.
Q2: Can external hemorrhoids go away on their own? Mild cases of external hemorrhoids can often resolve on their own with self-care measures and lifestyle changes. However, more severe cases may require medical intervention.
Q3: What self-care measures can help alleviate symptoms of external hemorrhoids? Self-care measures include maintaining a high-fiber diet, drinking enough water, practicing good anal hygiene, and avoiding excessive straining during bowel movements.
Q4: When should I seek medical attention for external hemorrhoids? If you experience severe pain, persistent bleeding, or if self-care measures do not alleviate the symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and treatment.
Q5: Are there any surgical treatment options for external hemorrhoids? In some cases, surgical interventions such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or hemorrhoidectomy may be recommended if other treatments have not been effective.

